What is alternating current and direct current?
What is alternating current and direct current?
- A direct current flows in one direction only in a circuit.
- The magnitude Of a direct current may be
(a) constant
(b) changes with time - Figure shows the graph of current against time for some direct currents.
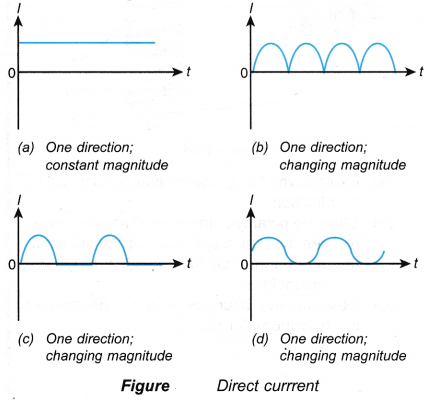
- An alternating current flows to and fro in two opposite directions in a circuit.
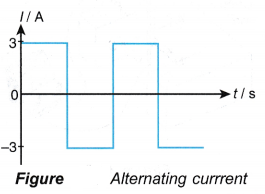
- Figure shows an alternating current with a constant magnitude of 3 A.
- Figure shows an alternating current with a magnitude that changes with time.
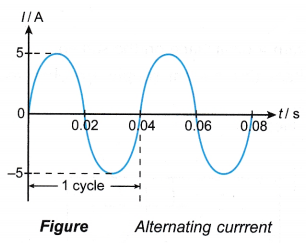 (a) The amplitude of the current or the peak current is Ip = 5 A
(a) The amplitude of the current or the peak current is Ip = 5 A
(b) The time for one cycle is, T = 0.04 s
(c) The frequency of the alternating current is given by:
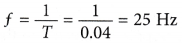
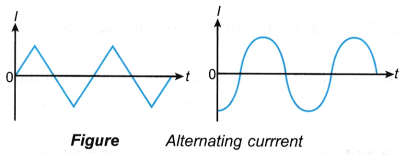
- Figure gives more examples of alternating currents.
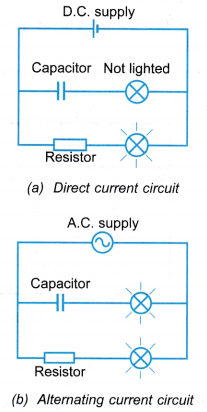
- An alternating current can flow through both a resistor and a capacitor whereas a direct current can flow through a resistor only.
People also ask
- What is the electromagnetic induction?
- What is Faraday’s law?
- What are the laws of electromagnetic induction?
- What is Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction?
- What is the Working Principle of AC Generator?
- What is the Working Principle of DC Generator?
- What is the Principle of DC Motor?
- Describe the turning effect on a current carrying coil in a magnetic field
- What is magnetic force on a current carrying conductor?
- What is the Meaning of Magnetic Force?
- What factors affect the strength of an electromagnet?
- What is the Magnetic Field?
- What Is Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current?
- Oersted Experiment on Magnetic Effect of Current
- How do you Determine the Direction of the Magnetic Field?
Alternating Current and Direct Current Experiment
Aim: To compare the output generated by a direct current source and an alternating current source.
Materials: Two 2.5 V bulbs, bulb holders
Apparatus: Battery holder with two dry cells, alternating current power supply, plug key switch, cathode ray oscilloscope (C.R.O.), connecting wires
Method: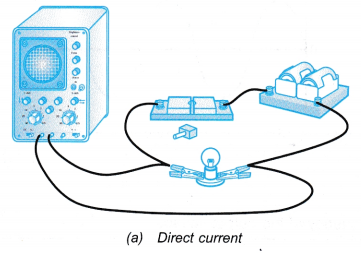
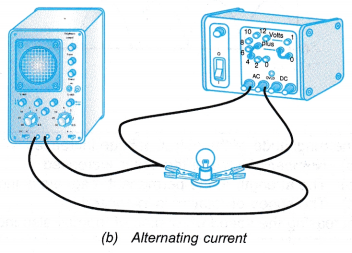
- The two circuits are set up as shown in Figure.
- The settings of the cathode ray oscilloscope are adjusted to obtain a clear trace on the screen.
- The traces formed by the output from the battery and the alternating current supply are observed and compared.
- The trace displayed on the screen of the oscilloscopes are sketched.
Observation: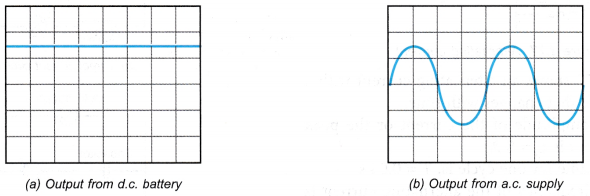 Discussion:
Discussion:
- The battery made up of two dry cells is a direct current source. The power supply connected to the mains supply delivers alternating current.
- Both the bulbs are lighted up. Therefore direct current and alternating current can flow through the filament of a bulb and produce a heating effect.
- The direct current flows in one direction only. The direction of the alternating current changes with time.
- The magnitude of the direct current remains constant. The magnitude of the alternating current changes between zero and a maximum value.
Conclusion:
A direct current flows in one direction only but the direction of an alternating current changes with time.
The post What is alternating current and direct current? appeared first on A Plus Topper.
from A Plus Topper
via Learning Made Simple 360
*Note that these contents are Autoblogged from A Plus Topper and cannot be edited.
Join the conversation